目录
显示
题目链接
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P2765
题解
不管咋样,我们先画一下图找找规律。
如果 \(x\) 能放在 \(y\) 上面,就从 \(y\) 向 \(x\) 连一条边。
比如样例对应的情况是这样的:
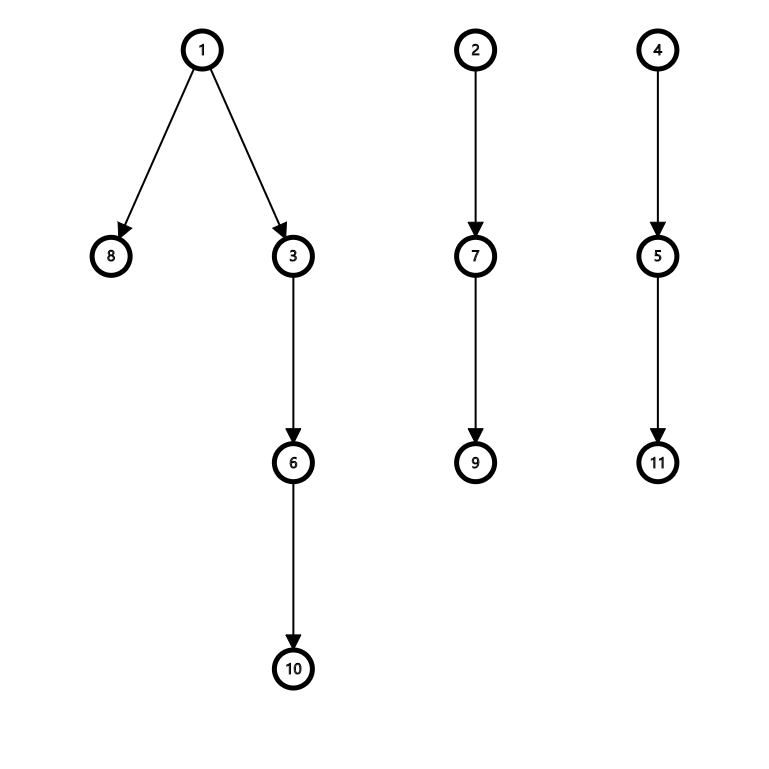
我们的目标是让我们用到的柱子数最少。也就是说,本题的任务是找一个 DAG 的(不重复的)最小路径覆盖。
因此我们可以这样做:我们每次动态加入一个点,并连接满足题意的边。跑 DAG 的最小路径覆盖,当最小路径覆盖数大于 \(n\) 时(也就是说 \(n\) 个柱子放不下了)则停止。
DAG 的最小路径覆盖可以参考 最小路径覆盖问题 一题。
本题中加点和加边是动态进行的,我们只需在上一次的残量网络上跑流就行。
本题还要输出方案。我们只需在残量网络上求出每个点的后继节点即可。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
struct edge
{
int v,w,next;
}e[100005];
int s=5e4+1,t=5e4+2,cnt=1;
int head[100005],dep[100005],vis[100005],cur[100005],nxt[100005];
void addedge(int u,int v,int w)
{
e[++cnt].v=v;
e[cnt].w=w;
e[cnt].next=head[u];
head[u]=cnt;
}
bool bfs()
{
queue<int> q;
memset(dep,INF,sizeof(dep));
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
memcpy(cur,head,sizeof(head));
dep[s]=0;
vis[s]=1;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty())
{
int p=q.front();
q.pop();
vis[p]=0;
for(int i=head[p];i;i=e[i].next)
if(dep[e[i].v]>dep[p]+1&&e[i].w)
{
dep[e[i].v]=dep[p]+1;
if(!vis[e[i].v])
{
vis[e[i].v]=1;
q.push(e[i].v);
}
}
}
if(dep[t]==INF)return 0;
return 1;
}
int dfs(int p,int w)
{
if(p==t)return w;
int used=0;
for(int i=cur[p];i;i=e[i].next)
{
cur[p]=i;
if(dep[e[i].v]==dep[p]+1&&e[i].w)
{
int flow=dfs(e[i].v,min(w-used,e[i].w));
if(flow)
{
used+=flow;
e[i].w-=flow;
e[i^1].w+=flow;
if(used==w)break;
}
}
}
return used;
}
bool check(int x)
{
for(int i=1;i*i<=x;i++)
if(i*i==x)return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int ans=1,num=0;
while(1)
{
int p=ans*2-1,q=ans*2;
addedge(s,p,1);
addedge(p,s,0);
addedge(q,t,1);
addedge(t,q,0);
for(int i=1;i<ans;i++)
if(check(ans+i))
{
addedge(i*2-1,q,1);
addedge(q,i*2-1,0);
}
while(bfs())
num+=dfs(s,INF);
if(ans-num>n)
{
printf("%d",ans-1);
for(int u=1;u<ans;u++)
for(int i=head[u*2-1];i;i=e[i].next)
if(e[i].v/2<ans&&!e[i].w)nxt[u]=e[i].v/2;
for(int i=1;i<ans;i++)
for(int j=i;j&&!vis[j];j=nxt[j])
{
if(j==i)puts("");
printf("%d ",j);
vis[j]=1;
}
return 0;
}
ans++;
}
}